This section demonstrate how to set up a complete connection with a SQL Server database step by step, allowing users to edit data, create and delete objects.
The test scenario uses a database containing a list of activities with planned start and finish dates, and a list of sub tasks or "Rules of credit" for each activity. The users will be able to report actual start and finish of each activity and progress of each rule of credit. Additionally the users will be able to add or remove rules of credits for each activity by executing stored procedures on the server.
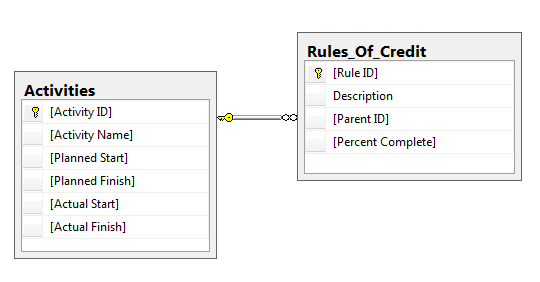
For the demonstration we will use a database with 2 tables, Activities and Rules_Of_Credit:
The following diagram summarises the set up:
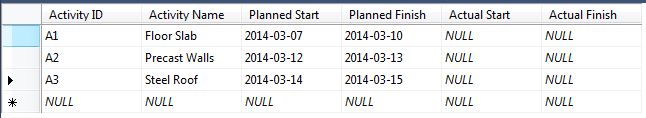
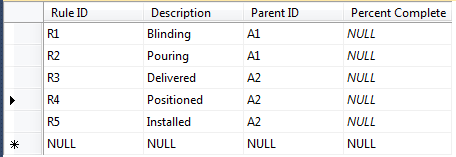
The 2 tables are loaded with sample data:
Start by creating a New Microsoft SQL Server DataSource:
You can now define the Read query to load data from the server
The user will have to see the data from both tables, with the rules of credit for each activity. To show the data from both the Activities and the Rules_Of_Credit tables, in the Read tab, we will use the following JOIN query:
SELECT *
FROM Activities LEFT JOIN Rules_Of_Credit
ON Activities.[Activity ID] = Rules_Of_Credit.[Parent ID]
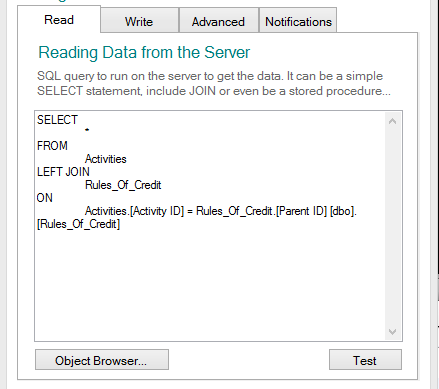
If you are unsure of the tables, views or columns names, you can use the Object Browser to get a list of the available objects. from the Object Browser you can insert an object name in your query by double clicking it in the tree or by selecting multiple objects and clicking Use Selected.
This set-up is sufficient to define a read-only connection. To end the configuration here you can click OK to close dialogue, then double click the DataView node in the Sources Manager Tree to activate the DataView.
If you are not already in the SQL Configuration Dialogue, right click the DataView node in the Sources Manager Tree and click Configure to reopen it.
To authorise the users to modify the Actual Start, Actual Finish and Percent Complete columns we need to provide the update details for the 3 columns from the Write tab:

Using the See Permissions button, you can access the list of columns on the server with access permissions, owning table and table key. You can add columns to the Write permission of the DataView from this list by double clicking the column to add or by selecting several columns and clicking Use Selected.
|
|
Although the dialogue will not prevent you from adding columns for which you do not have write permissions to the list of editable columns, this will not override the server permissions, and an error will be raised if you later try to change the values of such a column. |
|
This set-up is sufficient to define a read-only connection. To end the configuration here you can click OK to close dialogue, then double click the DataView node in the Sources Manager Tree to activate the DataView.
To learn more about editing value, check the Editing Properties of the DataSource section.
To authorise the users to create and delete "Rules of Credit", we can now define Actions.
We will create 2 actions that will execute stored procedures on the server, respectively named spCreateRuleOfCredit and spDeleteRuleOfCredit.
|
|
The procedures names must match stored procedures on your server. If the database that you are using does not have stored procedures to execute, you can type a SQL Statement instead of the procedure name. |
|
The creation procedure takes 2 arguments, the ID of the parent activity, @ParentID, and a description for the rule, @RuleOfCredit
The Parent Activity ID must be the ID of an existing activity. To enforce it we will lock the parameter value to the Activity ID of the selected row in the grid when the action is ran:
The deletion procedure only take 1 argument @RuleID for which we define a similar Default Mode using the Rule ID field of the selected row. This parameter is defined as Locked so it will not be editable. As a result, when deleting a rule of credit, the user will be prompted for confirmation with the Rule ID of the selected row displayed but won't be able to modify it.
The Rule ID is not very informative as it is only a number. To make it easier for the user to identify and confirm what rule is being deleted we can add Reference parameters to display more meaningful information. To add a Reference parameter:
Repeat those steps with a second Reference parameter named 'Of Activity' which will default to the selected row Activity Name.
See the section on Actions Parameter to learn more about editing types for parameters.
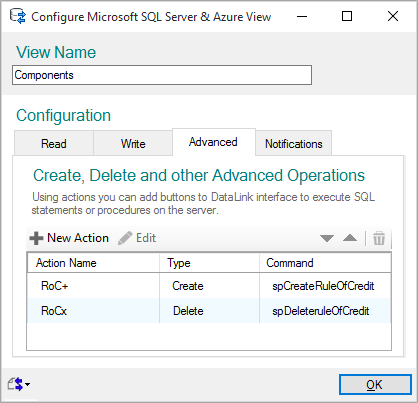
We have now finished configuring the Advanced section, we can head back to the BimSens grid.
Click OK to close dialogue, then double click the DataView node in the Sources Manager Tree to activate the DataView.
The 2 Actions button Create ![]() and Delete
and Delete ![]() are now available with their respective items RoC+ and RoCx. Each will open a dialogue to request user input or confirmation with the Required, Locked and Reference parameters.
are now available with their respective items RoC+ and RoCx. Each will open a dialogue to request user input or confirmation with the Required, Locked and Reference parameters.
|
|
Use the Import / Export button You can use this method to set-up multiple user profiles with different permissions but configure the root only once. For instance you can create one configuration file only allowing reporting of progress, and another for admin users allowing to create and delete rules of credit. |
|
SQL Server DataSource support change Notifications, and can be automatically refreshed, including re-apply a Colour Filter when a change is detected on the DataSource.
See the Walk through: Set up Notifications on SQL Server for more information.